Colors and Textures
Materials
Materials allow you to cover your meshes in color and texture and they need light to be seen. One material can be used to cover as many meshes as you wish.
Reactions to light
Whether the material is a color or a texture there are different ways it can react to light.
- Diffuse - the basic color or texture of the material;
- Specular - the highlight given to the material;
- Emissive - the color or texture of the material as if self lit;
- Ambient - the color or texture of the material lit by the environmental background lighting.
Diffuse and Specular material require a light source to be created.
Ambient color requires the ambient color of the scene to be set, giving the environmental background lighting.
scene.ambientColor = new BABYLON.Color3(1, 1, 1);
- Transparency - the level that you can see through the material can be set and for textures images with transparent sections can be used that so that appropriate parts of the material are invisible. This requires an alpha property to be set.
Color
Create a material using
var myMaterial = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("myMaterial", scene);
Set the material color using one, some or all of diffuseColor, specularColor, emissiveColor and ambientColor. Remember that ambientColor will only apply if the scene ambient color has been set.
var myMaterial = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("myMaterial", scene);
myMaterial.diffuseColor = new BABYLON.Color3(1, 0, 1);
myMaterial.specularColor = new BABYLON.Color3(0.5, 0.6, 0.87);
myMaterial.emissiveColor = new BABYLON.Color3(1, 1, 1);
myMaterial.ambientColor = new BABYLON.Color3(0.23, 0.98, 0.53);
mesh.material = myMaterial;
Diffuse Color Example
To give an idea how material diffuse color reacts to diffuse light color the following Playground Example -
shows how
| Yellow Material | Purple Material |
| Cyan Material | White Material |
react to white, red, green and blue diffuse spot lights. Notice how the viewing angle adjusts the lighting.
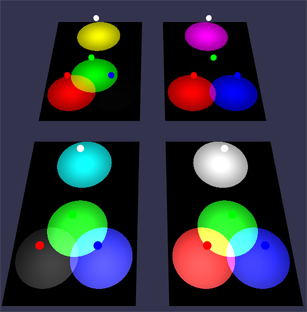
Ambient Color Example
In this playground example -
all spheres are lit by the same hemisphereic light, with diffuse red and groundColor green. The first sphere has no ambient color, the middle has red ambient color defined on its material and the one on the right has material with green ambient color. The scene ambient color, which must be present, is white. When a scene ambient color component is set to 0, for example red, then whatever the value for red in the material ambient color it will have no effect.
Transparent Color Example
Transparency is achieved by setting a materials alpha property from 0 (invisible) to 1 (opaque).
var myMaterial.alpha = 0.5;
Playground Example Transparency -
Texture
Textures are formed using a saved image.
Create a material using
var myMaterial = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("myMaterial", scene);
Set the material texture using one, some or all of diffuseTexture, specularTexture, emissiveTexture and ambientTexture. Notice that ambientTexture is applied without the scene ambient color having been set.
var myMaterial = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("myMaterial", scene);
myMaterial.diffuseTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("PATH TO IMAGE", scene);
myMaterial.specularTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("PATH TO IMAGE", scene);
myMaterial.emissiveTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("PATH TO IMAGE", scene);
myMaterial.ambientTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("PATH TO IMAGE", scene);
mesh.material = myMaterial;
Texture Example
In this playground example -
all spheres are lit by the same hemisphereic light, with diffuse red and groundColor green. The first sphere has a diffuse texture, the middle an emissive texture and the one on the right has material with red diffuse color an an ambient texture.

Transparent Texture Examples
As for colors the transparency is achieved by setting a materials alpha property from 0 (invisible) to 1 (opaque).
var myMaterial.alpha = 0.5;
Playground Example Transparency -
In addition the image used for the texture might already have a transparency setting, such as this picture of a dog from wikimedia commons, which has a transparent background;

In this case we set the hasAlpha property of the texture to true.
var myMaterial.diffuseTexture.hasAlpha = true;
Playground Example Transparent Background -
For the back faces of the cube to be visible through the transparent areas of the front faces we have to deal with back face culling.
Back Face Culling
This is a method for efficiently drawing the 2D screen rendering of the 3D model. Usually there is no need to draw the back face of a cube, or other object, as it will be hidden by the front face. In BabylonJS the default setting is, as you might expect, set to true.
Looking at the images below, when the material propery backFaceCulling is true you can see that the transparent areas around the dog are still transparent, you can see the background through them. However you cannot see the images on the back faces as they have been culled (or removed). When backFaceCulling is false the back faces are not removed during rendering so they can be seen through the transparent areas of the front faces.
| Back Face Culling True | Back Face Culling False |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Playground Example Back Ground Culling True -
WireFrame
You can see a mesh in wireframe mode by using:
materialSphere1.wireframe = true;
